Carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP) are highly attractive for various industries in demanding application fields due to their unique balance of rigidity, mechanical strength and light weight – also compared with conventional glass fiber reinforced plastics. However, CFRPs are expensive and challenging from a recycling perspective, as it is difficult to extract the carbon fibers from the resin after usage.
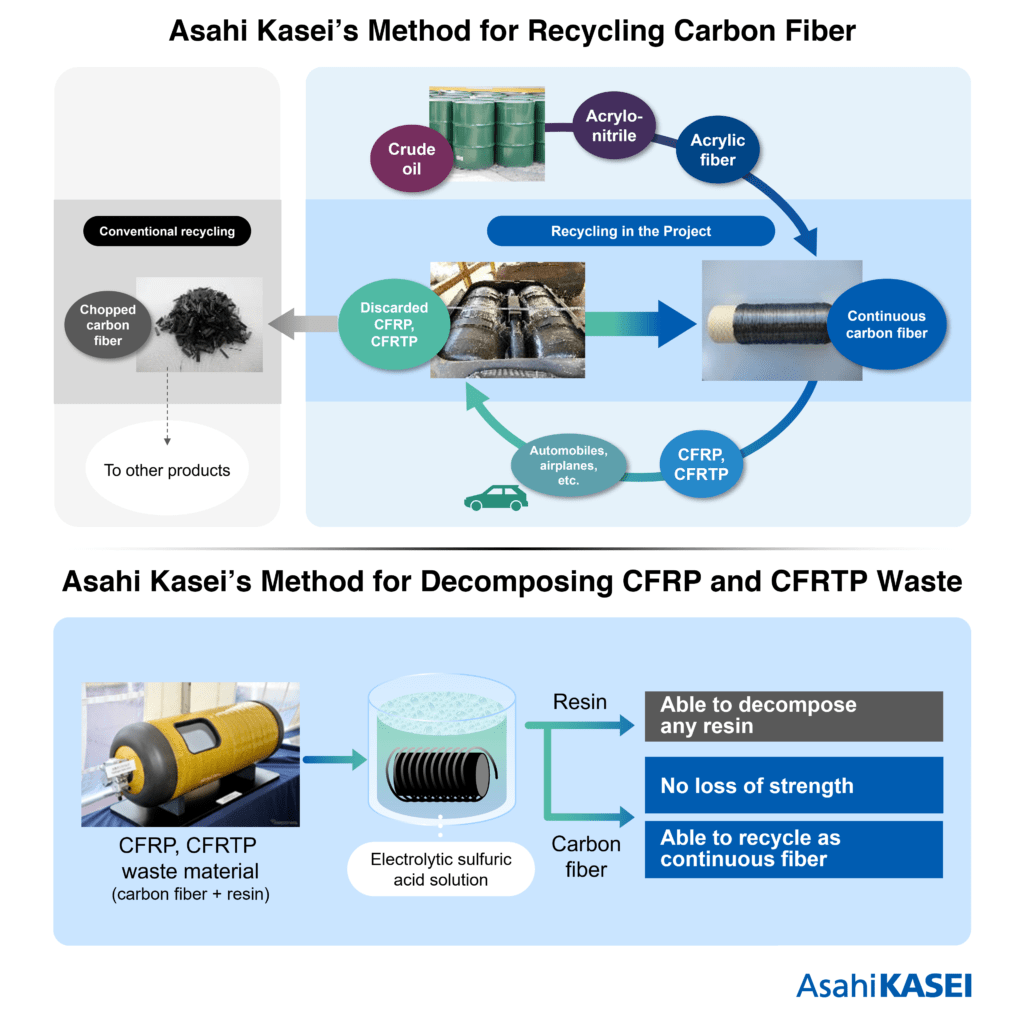
Together with its project partners at the National Institute of Technology at Kitakyushu College and the Tokyo University of Science, Asahi Kasei has developed a recycling method that allows car-bon fibers to be extracted from CFRP or carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastics (CFRTP) used in automobiles. This results in high-quality, inexpensive continuous carbon fiber that can be recycled perpetually, contributing to circular economy. Unlike carbon fiber that is chopped up during the recycling process, Asahi Kasei’s method allows carbon fiber to be extracted from a plastic com-pound seamlessly, resulting in continuous strands of carbon fiber that can be reapplied in exactly the same manner while retaining properties identical to the original substance.
The conventional technologies for recycling carbon fibers by chopping and re-applying them results in a product with lower quality and less durability, insufficient for high-performance applications. To address this issue, Asahi Kasei has developed an “electrolyzed sulfuric acid solution method” that allows the carbon fiber to retain its original strength and continuous nature while fully decomposing the resin the carbon fiber is embedded in. This allows for its continued use in high-performance applications and presents an inexpensive, circular solution to the end-of-life dilemma of carbon fiber plastic compounds. Thus, these carbon fiber compounds present in vehicles for weight reduction. It can be easily and inexpensively be broken down at end-of-vehicle-life and reapplied to new vehicles in the future.
In addition, Asahi Kasei is developing a carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic unidirectional tape (CFRTP-UD tape) that utilizes both recycled continuous carbon fiber and the company’s Leona™ polyamide resin. Boasting a higher strength than metal, this CFRTP-UD tape can be applied to automobile frames and bodies, further enabling the recycling of end-of-vehicle-life parts into differ-ent, new automobile parts. This presents a solution to the long-term challenge that carbon fiber usage for vehicles has posed on the industry and is expected to economically benefit and strengthen carbon fiber’s usage within the automobile industry on a global scale. Moving forward, Asahi Kasei will perform demonstrations and develop the business, aiming for practical application around 2030.
About the Asahi Kasei Corporation
The Asahi Kasei Group contributes to life and living for people around the world. Since its founda-tion in 1922 with ammonia and cellulose fiber businesses, Asahi Kasei has consistently grown through the proactive transformation of its business portfolio to meet the evolving needs of every age. With more than 46,000 employees around the world, the company contributes to a sustaina-ble society by providing solutions to the world’s challenges through its three business sectors of Material, Homes, and Health Care. Its Materials sector, comprised of Environmental Solutions, Mobility & Industrial, and Life Innovation, includes a wide array of products from battery separators and biodegradable textiles to engineering plastics and sound solutions. For more information, visit www.asahi-kasei.com.
Asahi Kasei is also dedicated to sustainability initiatives and is contributing to reaching a carbon neutral society by 2050. To learn more, visit https://www.asahi-kasei.com/













More Stories
BRANO and DOMO join forces to replace aluminum with TECHNYL® polyamide
trinamiX – will cars function like Smartwatches in the future?
Motorcycle Defects That Can Lead to Catastrophic Accidents